-
Research Article

- Energy-saving potential of a high-temperature dual-tank air-source heat pump for greenhouse heating: a field study in Korea
- Kyoung-Joong Kim, Kyu-Ho Lee, Md Nasim Reza, Dae-Hyun Lee, Sun-Ok Chung, Hee-Bok Lee
- Smart greenhouse technologies are rapidly expanding, significantly increasing the demand for stable and economically feasible heating solutions, for subtropical crops requiring precise …
- Smart greenhouse technologies are rapidly expanding, significantly increasing the demand for stable and economically feasible heating solutions, for subtropical crops requiring precise temperature management. This study evaluates the field performance and economic feasibility of a dual thermal storage high-temperature air-source heat pump (ASHP) system implemented in a smart greenhouse located in Boryeong, Chungnam, South Korea. Prior to 2018, the facility used a traditional diesel boiler in combination with electric radiators to maintain optimal indoor conditions for subtropical crops such as coffee and bananas. In 2018, this conventional system was replaced with an advanced dual thermal storage ASHP system, specifically designed to effectively manage variable heating loads and ensure consistent indoor environmental conditions. Field evaluations were conducted over a 57-day period from January 5 to March 2, 2025, during which critical parameters including indoor temperature stability, system energy efficiency (Coefficient of Performance, COP), and operational costs were meticulously monitored and analyzed. Despite external temperature variations ranging between 0°C and 20°C, the ASHP system maintained stable greenhouse temperatures consistently above the target threshold of 20°C. The average COP recorded during this period was approximately 1.28, indicating robust energy efficiency. Moreover, the economic analysis demonstrated substantial cost savings, revealing a reduction of approximately 67% in operating expenses compared to the previous diesel boiler system. These results highlight the practical applicability and economic advantages of dual thermal storage ASHP systems in smart agricultural environments. The findings further support the broader implementation of sustainable and energy-efficient heating solutions in smart greenhouse operations, emphasizing their potential for significant reductions in operating costs and enhancements in environmental sustainability. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
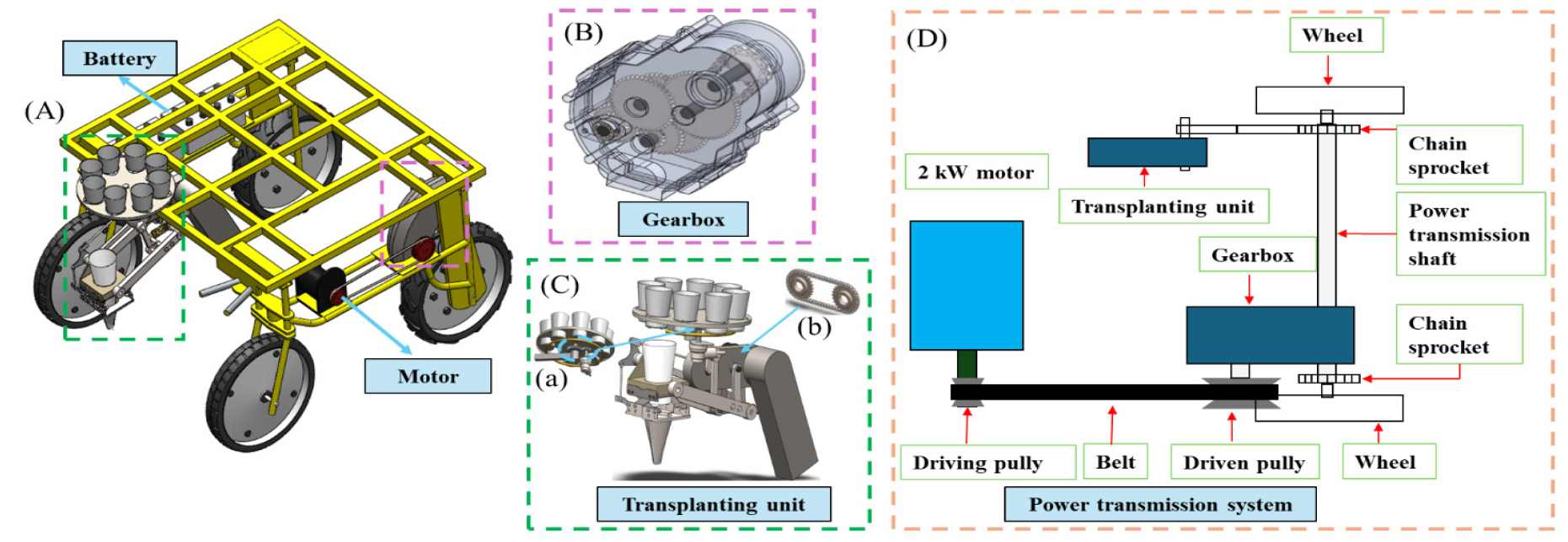
- Geometric optimization and power transmission analysis of a gearbox for 2-kW semi-automatic biodegradable potted cabbage transplanter
- Md Razob Ali, Md Nasim Reza, Md Aminur Rahman, Beom-Sun Kang, Hee-Bok Lee, Sun-Ok Chung, Kanghee Jeong
- The design and performance of multi-stage gearboxes are essential for ensuring efficiency, durability, and reliability in agricultural machinery. This study proposed a …
- The design and performance of multi-stage gearboxes are essential for ensuring efficiency, durability, and reliability in agricultural machinery. This study proposed a framework for geometric optimization and power transmission analysis of a three-stage spur gear reducer developed for a 2-kW semi-automatic cabbage transplanter. Gear sizing was conducted in accordance with ISO 6336, with fine sizing validated through mechanical simulation to assess bending strength, contact stress, and safety factors. Optimization considered key design parameters, including module, face width, center distance, and tooth numbers, to balance load-carrying capacity, weight, and manufacturability, yielding 386, 278, and 418 feasible solutions for the first, second, and third stages, respectively. The optimized designs achieved torque capacities of 16–17 Nm (Stage 1), 12 Nm (Stage 2), and 12–13 Nm (Stage 3), with safety factors consistently above ISO thresholds. Root safety factors exceeded 5.0 across all stages, while flank safety factors ranged from 2.0 to 2.9, indicating surface durability as the governing criterion. Power loss and efficiency, evaluated using ISO/TR 14179-2, showed total losses of 30.1 W and an overall efficiency of 95.4%, dominated by meshing losses, with bearing and shaft losses negligible. The results demonstrate that systematic gear optimization ensures high transmission efficiency, reduced mass, and robust safety margins, offering a transferable methodology for lightweight and durable drivetrain design in agricultural machinery. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
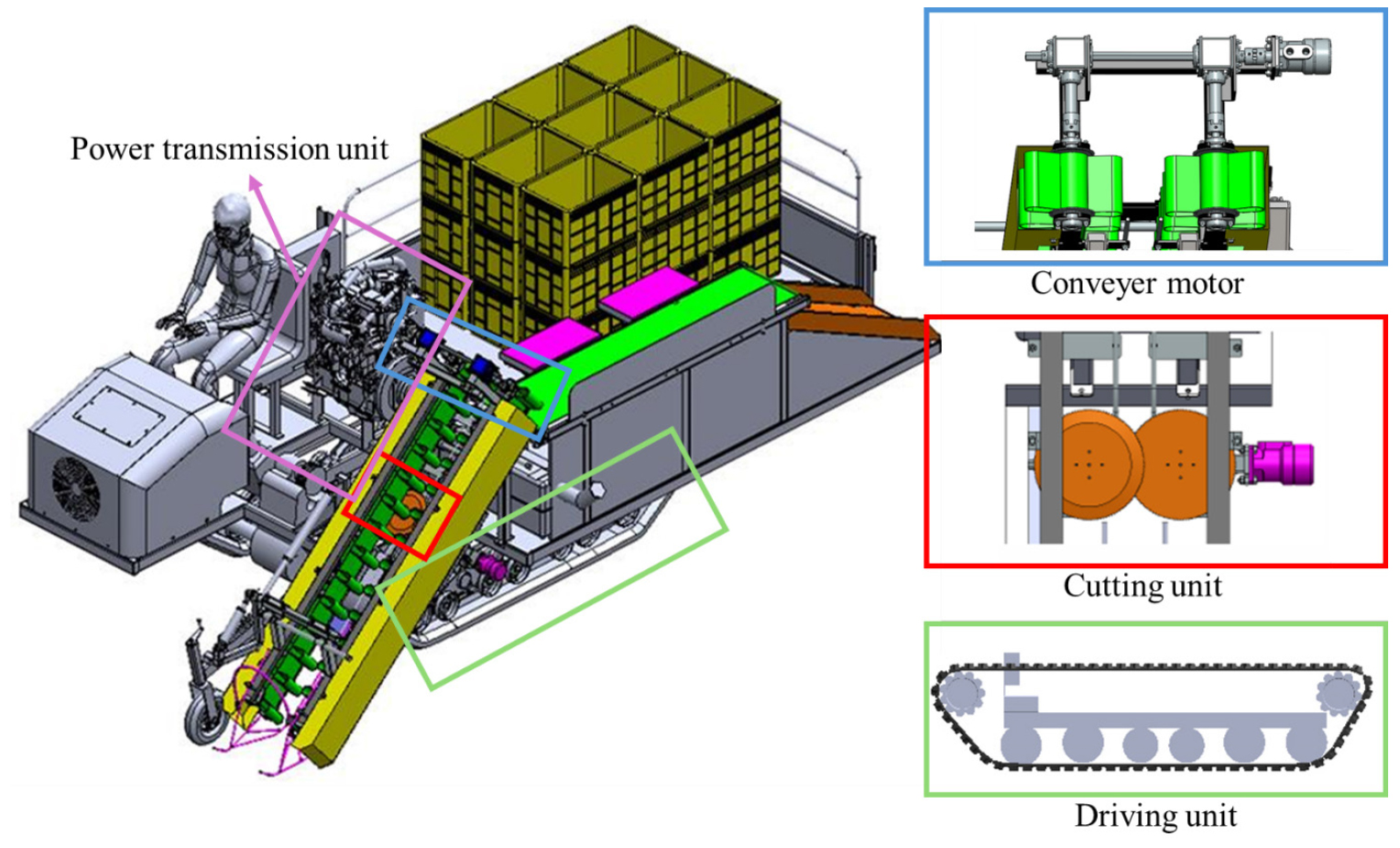
- Structural analysis of key power transmission components of a 36.8-kW 1-row self-propelled cabbage harvester
- Md Razob Ali, Md Nasim Reza, Md Aminur Rahman, Da-Hye Jeong, Og Ran Park, Sun-Ok Chung, Kanghee Jeong
- This study evaluates the structural and efficiency performance of the main power transmission components of a self-propelled cabbage harvester, namely the cutting …
- This study evaluates the structural and efficiency performance of the main power transmission components of a self-propelled cabbage harvester, namely the cutting blades, motor shaft, driving sprocket, and gearbox. Finite element analysis (FEA), KISSsoft simulations, and field testing were employed to assess strength, durability, and energy efficiency under realistic harvesting conditions. Three-dimensional models of the cutting blades, shaft, and sprocket were created in mechanical design software, and finite element simulations were conducted in simulation to determine stress distribution, deformation, and fatigue life. Mesh convergence studies ensured accuracy, while material properties such as Young’s modulus, yield strength, and Poisson’s ratio were defined from standards. The gearbox was analyzed in KISSsoft 2018 using ISO 6336 guidelines to calculate transmission efficiency, root and flank safety factors, and power loss contributions from gears, shafts, and bearings. Field tests were carried out to validate the simulated results and to evaluate cutting and picking quality under real soil and crop conditions. Results showed that the continuous-edge disc blade performed better than the segmented-edge blade, with lower stress (3.05 MPa) and a higher factor of safety (115.38). The motor shaft safely transmitted 200 Nm torque at 300 rpm with an FOS of 119 and fatigue life above 1,000,000 cycles. The sprocket exhibited very low stress (0.38 MPa) and an FOS of 146. Gearbox analysis demonstrated an efficiency of 97.99% with an output power of 10.26 kW at 200 Nm, where gear contact losses dominated. The power transmission system proved structurally robust, energy-efficient, and capable of reliable long-term use in cabbage harvesting. The harvester design is safe, durable, and field-ready with scope for further optimization. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article
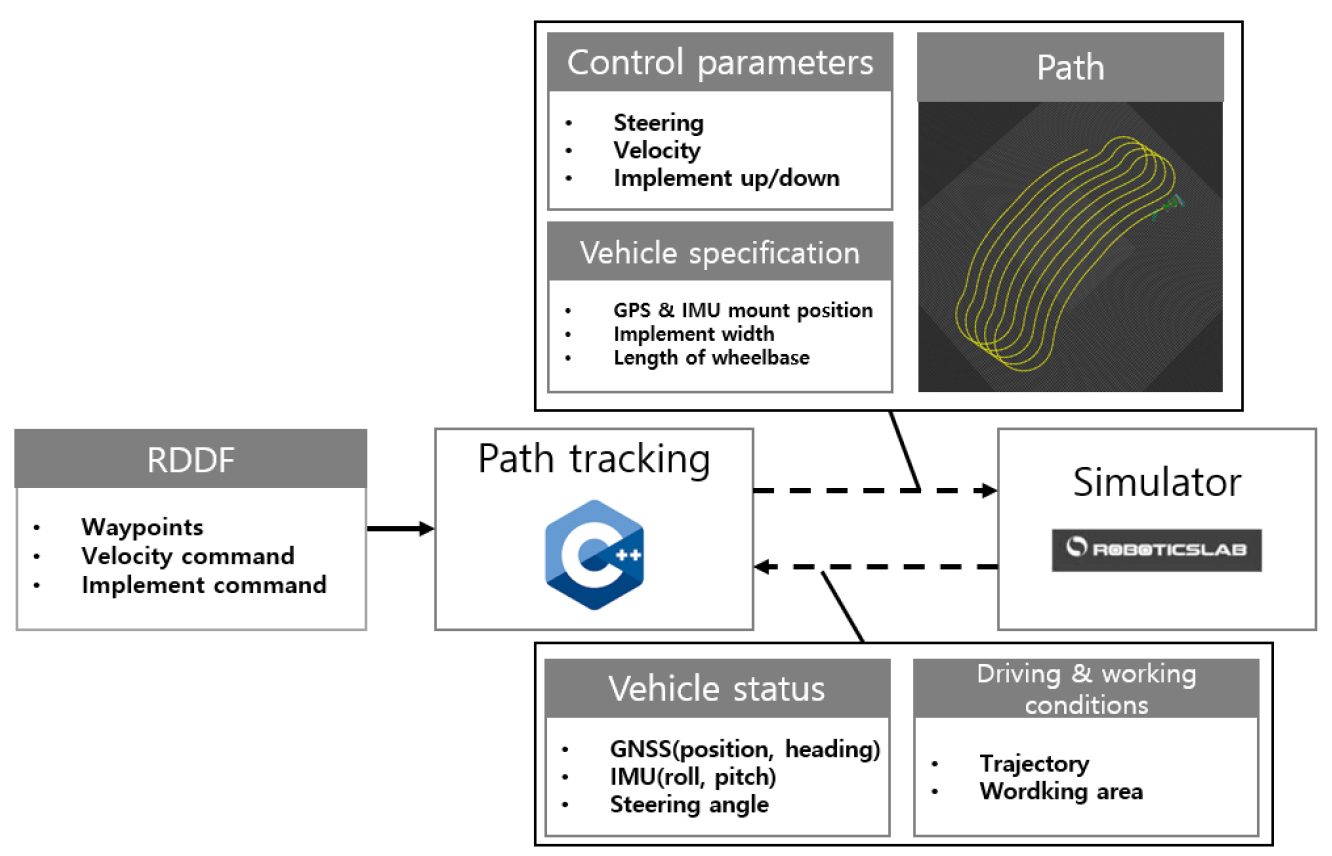
- Development of a curved path generation and tracking algorithm for an auto-guided tractor
- Kyeong-Min Kang, Yong-Hyun Kim, Changho Yun, Hak-Jin Kim
- In domestic farmland environments, fields often have irregular shapes and slopes, making it difficult to apply conventional path generation and tracking algorithms …
- In domestic farmland environments, fields often have irregular shapes and slopes, making it difficult to apply conventional path generation and tracking algorithms for auto-guided tractors. Most existing algorithms have been developed assuming flat and straight working paths, which limits their applicability to irregularly curved or sloped farmlands. To address these limitations, this study developed a curved path generation and tracking algorithm to enhance the applicability of auto-guided tractors in complex field conditions. To generate curved paths, a reference path was first created based on the manual driving data. Additional working and headland turning paths were then generated by considering the implement’s working width and the field dimensions. To enable path tracking on curved and sloped terrain, path curvature was defined and integrated into an implement-centered path tracking algorithm. The proposed path generation and tracking algorithms were tested through both simulation and field experiments. When curvature was applied, the field experiment results showed that the implement’s tracking error in curved working path decreased by 33.7%, and the total error for the entire path—including headland turns—was reduced by 38.9% compared to the case without curvature application. These results demonstrate significant improvements in both tracking accuracy and operational efficiency. Overall, the findings indicate that the developed algorithm enhances the tracking performance of auto-guided tractors and extends their applicability to irregular farmland, including convex, concave, and sloped fields. - COLLAPSE
-
Review Article
- A comprehensive review of legume crop harvesting machinery: Development, Intelligent mechanization, and future prospects
- Jinho Son, Ju-Hee Lee, Seok-Ho Kang, Won-Yeol Choi, Bumseok Park, Hyung-Gyu Park, Yushin Ha
- Legume crops are essential components of global agriculture, providing sustainable plant-based protein and enhancing soil fertility. However, harvesting remains a complex and …
- Legume crops are essential components of global agriculture, providing sustainable plant-based protein and enhancing soil fertility. However, harvesting remains a complex and loss-prone stage due to diverse plant morphologies. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the evolution of legume harvesting machinery, focusing on the four major categories defined by the FAO: soybeans, groundnuts, pulses, and fresh legumes. We trace the progression from manual operations to modern intelligent systems, highlighting engineering adaptations for different crop structures. Soybean mechanization has advanced through flexible headers for low pod recovery, while groundnut machinery evolved with specialized digger-shaker-inverter mechanisms. Pulse harvesting relies on gentle threshing to reduce breakage, whereas fresh legume systems integrate low-impact handling to preserve quality. Despite remarkable progress, persistent challenges—including high pod shattering, uneven crop maturity, and performance instability under varying field conditions—continue to limit harvesting efficiency. We identify emerging trends in intelligent mechanization, such as multi-sensor data fusion and machine learning-based optimization, as promising pathways to address these limitations and ensure ergonomic operator protection. By synthesizing mechanical design principles with advances in automation, this review establishes a framework for developing future adaptive and sustainable legume harvesting systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Research Article

- Multiple Linear Regression models for estimating the plant height of red pepper using UAV-based multispectral imagery
- HoJun Kwon, Ye-Seong Kang, ChanSeok Ryu, ChangHyeok Park, GangIn Je
- Red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) is a major field crop in Korea; however, its productivity and cultivation area have recently declined …
- Red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) is a major field crop in Korea; however, its productivity and cultivation area have recently declined due to labor shortages caused by an aging population and climate variability. This study was conducted on the ‘Colormura’ cultivar, transplanted on April 29 in a farm field located in Bangyo-ri, Gimje-si. The objective was to develop a Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) model to estimate plant height—a key growth indicator highly correlated with yield—using vegetation indices derived from Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-based multispectral imagery. Plant height data and UAV multispectral images were collected at three time points: mid-June, mid-July, and mid-August. To evaluate the model's generalization performance, the data were partitioned into calibration and validation datasets at ratios of 8:2, 7:3, and 6:4, and performance was assessed using R2, RMSE, and MAPE. Because individual monthly analyses resulted in low generalization performance or overfitting, the model was constructed using time-series data spanning from June to August. The model utilizing PRI, TCARI, NDRE, and OSAVI exhibited the best performance. Notably, the RedEdge-based indices, NDRE and TCARI, made significant contributions to the prediction of plant height. This study demonstrates the potential of estimating red pepper growth using UAV multispectral data. Future research should focus on enhancing model performance by expanding the dataset and applying diverse analytical techniques. - COLLAPSE
-
Review Article
- Non-contact yield measurement during harvesting operations for major root vegetables in Korea: A review
- Pabel Kanti Dey, Md Nasim Reza, Ezatullah Zakir, Samsuzzaman, Kyu-Ho Lee, Da-Hye Jeong, Sun-Ok Chung
- The increasing demand for food production amid declining labor availability and shrinking agricultural land necessitates the adoption of advanced monitoring and automation …
- The increasing demand for food production amid declining labor availability and shrinking agricultural land necessitates the adoption of advanced monitoring and automation technologies in root vegetable production. Root crops such as potato, radish, carrot, and sweet potato are vital to food security and dietary health in Korea; however, yield estimation traditionally relies on manual sampling and post-harvest weighing, leading to inefficiencies and limited spatial insight. This review presented an overview of non-contact yield monitoring techniques applicable to root vegetable crops, highlighting core sensing, data processing methods, and field integration approaches. Optical imaging, particularly RGB and RGB-D systems, currently offers cost-effective solutions for tuber detection, grading, and morphology measurement, though performance remains sensitive to illumination and soil variability. LiDAR-based techniques enable accurate 3D volumetric modeling but face constraints related to cost, vibration disturbances, and computational load. Ultrasonic, thermal, radar, and hyperspectral sensors provide complementary information on crop structure and physiological status but are best suited as auxiliary sources within multimodal frameworks. Data processing advancements, including deep learning based segmentation and sensor fusion, significantly improve real-time accuracy and robustness under dynamic harvesting conditions. In the context of Korea’s evolving mechanized agriculture, integrating these technologies into harvester platforms can provide spatially enabled, real-time yield intelligence to strengthen supply chain logistics and farm-level decision-making. The review concluded with key challenges and future directions to accelerate commercialization and adoption of smart yield monitoring systems for sustainable root crop production. - COLLAPSE
-
Review Article

- Moisture sensing technologies for grain storage: From single sensors to intelligent multisensory system
- Amiruddin Aziz, Gilbert Mugwaneza, Jean Claude Nshimiyimana, Alisabela Dhiya Rachmah, Tusan Park
- Moisture content is a critical parameter influencing grain quality during storage, as it directly affects microbial activity, respiration, and post-harvest deterioration. Accurate …
- Moisture content is a critical parameter influencing grain quality during storage, as it directly affects microbial activity, respiration, and post-harvest deterioration. Accurate and timely monitoring of grain moisture is therefore essential to minimize storage losses and preserve quality, particularly under long-term storage conditions. This study presents a systematic review and bibliometric analysis of moisture content sensing technologies applied to grain storage, covering research published between 2015 and 2024. A two-step methodological approach was adopted. First, a bibliometric analysis of 97 publications retrieved from the Scopus database was conducted to identify publication trends, research focus areas, and technological development patterns. Second, a systematic review following PRISMA guidelines was performed, resulting in the selection of 29 studies that specifically addressed sensor-based moisture measurement in grain storage. The selected studies were analyzed with respect to grain type, sensing principles, sensor configurations, and data processing approaches. The results reveal a clear transition from conventional single-parameter moisture sensing toward integrated monitoring systems that combine indirect sensing techniques, wireless communication, and data-driven models. Capacitive and equilibrium relative humidity (ERH) sensors remain the most commonly used approaches due to their simplicity and low cost; however, their sensitivity to environmental variability and calibration drift limits their reliability when used alone. Recent studies increasingly employ multisensor frameworks that integrate temperature, relative humidity, and carbon dioxide measurements, with CO2 emerging as a robust indicator of grain respiration and early quality deterioration. Machine learning models, particularly artificial neural networks and random forest algorithms, demonstrate strong performance in predicting moisture content and overall grain quality from multisensor data. Despite these advances, challenges related to sensor accuracy, long-term stability, calibration, and cost continue to hinder large-scale adoption, especially in developing regions. This review highlights the need for intelligent, low-cost multisensor systems to enable reliable, real-time grain storage monitoring and improved post-harvest management. - COLLAPSE
Journal Informaiton
 Precision Agriculture Science and Technology
Precision Agriculture Science and Technology
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Precision Agriculture Science and Technology
Precision Agriculture Science and Technology











